Linux Device Driver
tainted flags
參考資訊:
1. tainted kernels
example
BUG: unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at 0000000000000000 Oops: 0002 [#1] SMP PTI CPU: 0 PID: 4424 Comm: insmod Tainted: P W O 4.20.0-0.rc6.fc30 #1 Hardware name: Red Hat KVM, BIOS 0.5.1 01/01/2011 RIP: 0010:my_oops_init+0x13/0x1000 [kpanic] [...]
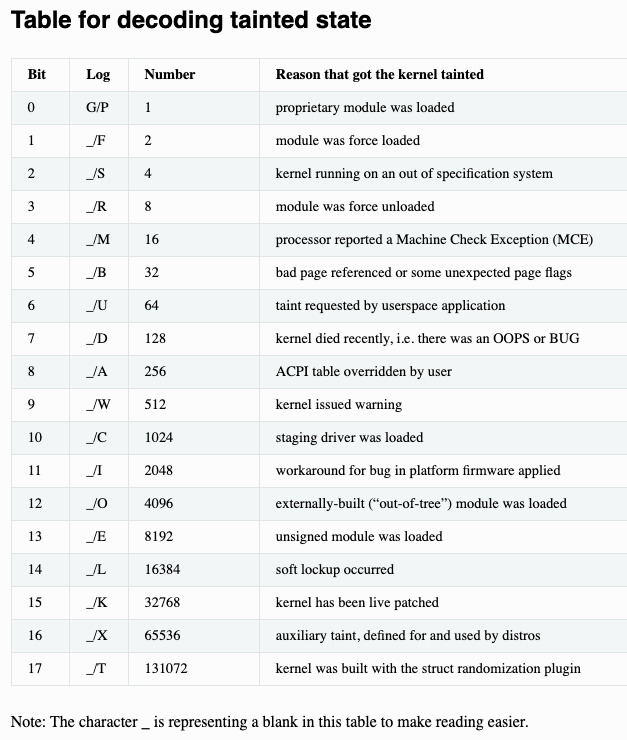
說明:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| G | if all modules loaded have a GPL or compatible license, P if any proprietary module has been loaded. Modules without a MODULE_LICENSE or with a MODULE_LICENSE that is not recognised by insmod as GPL compatible are assumed to be proprietary. |
| F | if any module was force loaded by insmod -f, ' ' if all modules were loaded normally. |
| S | if the kernel is running on a processor or system that is out of specification: hardware has been put into an unsupported configuration, therefore proper execution cannot be guaranteed. Kernel will be tainted if, for example: on x86: PAE is forced through forcepae on intel CPUs (such as Pentium M) which do not report PAE but may have a functional implementation, an SMP kernel is running on non officially capable SMP Athlon CPUs, MSRs are being poked at from userspace. on arm: kernel running on certain CPUs (such as Keystone 2) without having certain kernel features enabled. on arm64: there are mismatched hardware features between CPUs, the bootloader has booted CPUs in different modes. certain drivers are being used on non supported architectures (such as scsi/snic on something else than x86_64, scsi/ips on non x86/x86_64/itanium, have broken firmware settings for the irqchip/irq-gic on arm64 …). |
| R | if a module was force unloaded by rmmod -f, ' ' if all modules were unloaded normally. |
| M | if any processor has reported a Machine Check Exception, ' ' if no Machine Check Exceptions have occurred. |
| B | If a page-release function has found a bad page reference or some unexpected page flags. This indicates a hardware problem or a kernel bug; there should be other information in the log indicating why this tainting occurred. |
| U | if a user or user application specifically requested that the Tainted flag be set, ' ' otherwise. |
| D | if the kernel has died recently, i.e. there was an OOPS or BUG. |
| A | if an ACPI table has been overridden. |
| W | if a warning has previously been issued by the kernel. (Though some warnings may set more specific taint flags.) |
| C | if a staging driver has been loaded. |
| I | if the kernel is working around a severe bug in the platform firmware (BIOS or similar). |
| O | if an externally-built (“out-of-tree”) module has been loaded. |
| E | if an unsigned module has been loaded in a kernel supporting module signature. |
| L | if a soft lockup has previously occurred on the system. |
| K | if the kernel has been live patched. |
| X | Auxiliary taint, defined for and used by Linux distributors. |
| T | Kernel was build with the randstruct plugin, which can intentionally produce extremely unusual kernel structure layouts (even performance pathological ones), which is important to know when debugging. Set at build time. |